-
Maximal daily provision = 2-2.5 g/kg/day
- CAUTION: If providing >2 gram/kg/day (Weight risks/benefits with attending physician and family)
- Maximal infusion rate of 0.15-0.17 mg/kg/hour
- Maximal lipid-to-energy ratio of 25%.
-
Types of intravenous lipid emulsions ilipids available in the US:
- Intralipid (source of calories and essential fatty acids in patients who are parenteral nutrition dependent)
- SMOFlipid (source of calories and essential fatty acids in adults who cannot receive them via oral or enteral route in July 2016)
- Omegaven (Approved for children with PNALD in July 2018)
Intravenous lipid emulsion test dose intructions:
- Infuse at 0.1 mL/minute for the first 10-15 minutes (i.e., 1.5ml dose over 15 minutes …..which would run at a rate of 6 ml/hr).
- If no reaction, then increase to the anticipated hourly rate of intravenous lipid emulsion.
- Observe patient receiving intravenous lipid emusion for 1 hour.
|

https://www.fresenius-kabi.com/in/products/intralipid
If using Intralipid in patients with long-term PN dependence, consider IV lipid minimization for reduced exposure to phytosterols: Average dose 1 gram/kg/day over 1 week for prevention of PN associated liver disease.
If cholestasis occurs on IV lipid minimization with soybean-based IV lipid emulsion, short-term lipid cessation may result in improvement in hyperbilirubinemia but can lead to complications like essential fatty acid deficiency and poor growth.
- With short-term intravenous lipid emulsion cessation, consider checking fatty acid profile monthly and encourage enteral essential fat intake.
- If patient is stable for 2-3 months, may space out lab monitoring.
Typical dosing, soybean IV lipid dosing:
-
If 2-in-1, maximum daily 1 gram/kg/day
-
If 3-in-1, maximum daily 2 gram/kg/day

- Use 1.2 micron in-line filter.
- Concentration: 0.2 grams/mL (2kcal/mL)
- Dosage forms: 100 ml, 250 ml and 500 ml
Colomb V, Jobert-Giraud A, Lacaille F, Goulet O, Fournet JC, Ricour C. Role of lipid emulsions in cholestasis associated with long-term parenteral nutrition in children. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2000 Nov-Dec;24(6):345-50. PubMed PMID: 11071594.
Lam G, Strogach IG, Baron N, Thompson JF. Normal Growth and Essential Fatty Acid Status in Children With Intestinal Failure on Lipid Limitation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016 Feb;62(2):335-40. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000948. PubMed PMID: 26301616.
Rollins MD, Ward RM, Jackson WD, Mulroy CW, Spencer CP, Ying J, Greene T, Book LS. Effect of decreased parenteral soybean lipid emulsion on hepatic function in infants at risk for parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: a pilot study. J Pediatr Surg. 2013 Jun;48(6):1348-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.03.040. PubMed PMID: 23845629.

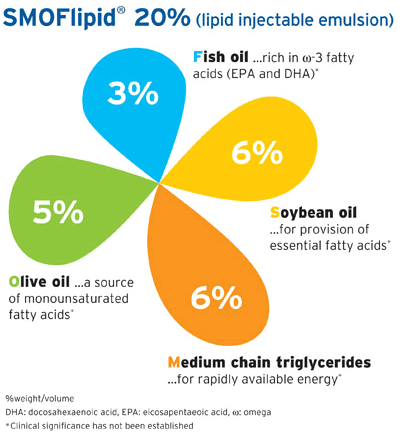
- Use 1.2 micron in-line filter.
- Concentration: 0.2 grams/mL (2kcal/mL)
- Dosage forms: 100 ml, 250 ml and 500 ml
Lam CKL, Church PC, Haliburton B, Chambers K, Martincevic I, Vresk L, Courtney-Martin G, Bandsma R, Avitzur Y, Wales PC, Mouzaki M. Long-term Exposure of Children to a Mixed Lipid Emulsion Is Less Hepatotoxic Than Soybean-based Lipid Emulsion. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018 Mar;66(3):501-504. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001799. PubMed PMID: 29470321.
Omegaven (Intravenous Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion)
FDA approved on June 27, 2018: Indicated as a source of calories and fatty acids in pediatric patients with parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis (PNAC)

https://www.fresenius-kabi.com/in/products/omegaven
Indication:
- Cholestasis due to parenteral nutrition (no other causes) with direct or conjugated bilirubin levels persistently ≧2 mg/dL (usually >1 week).
- There is no evidence to suggest Omegaven prevents PN associated liver injury. It should not be used prophylactically.
Dosage: 1 gram/kg/day until direct bilirubin is
Monitoring
- Check labs weekly if direct bilitubin > 2.0
- Check labs monthly if direct bilirubin
- Use 1.2 micron in-line filter.
- Concentration: 0.1 grams/mL (2kcal/mL)
- Dosage forms: 100 ml
- Can be infused along with PN
Drug related concerns:
- Prolonged bleeding has been reported in some patients taking high doses of enteral fish oil supplements.
- Hypertriglyceridemia -- hold lipids if triglycerids >1000
- Known hypersensitivity to fish or egg -- consider test dose.
ClinoLeic (80% olive oil and 20% soybean oil)
- Studied in pediatrics and adults.
- Not FDA approved in US..
- If triglycerides > 200mg/dL, then hold lipids for 4 hours, and recheck.
- If triglycerides remain elevated, consider decreasing intravenous lipid emulsion rate.
-
Neonates and malnourished patients may have difficulty clearing lipids due to decreased hepatic lipoprotein lipase activity
-
Consider supplementation with levocarnititine 8-16mg/kg/day
-
Consider supplementation of heparin to parentral nutrition (1 unit per mL) – induces lipoprotein lipase
-
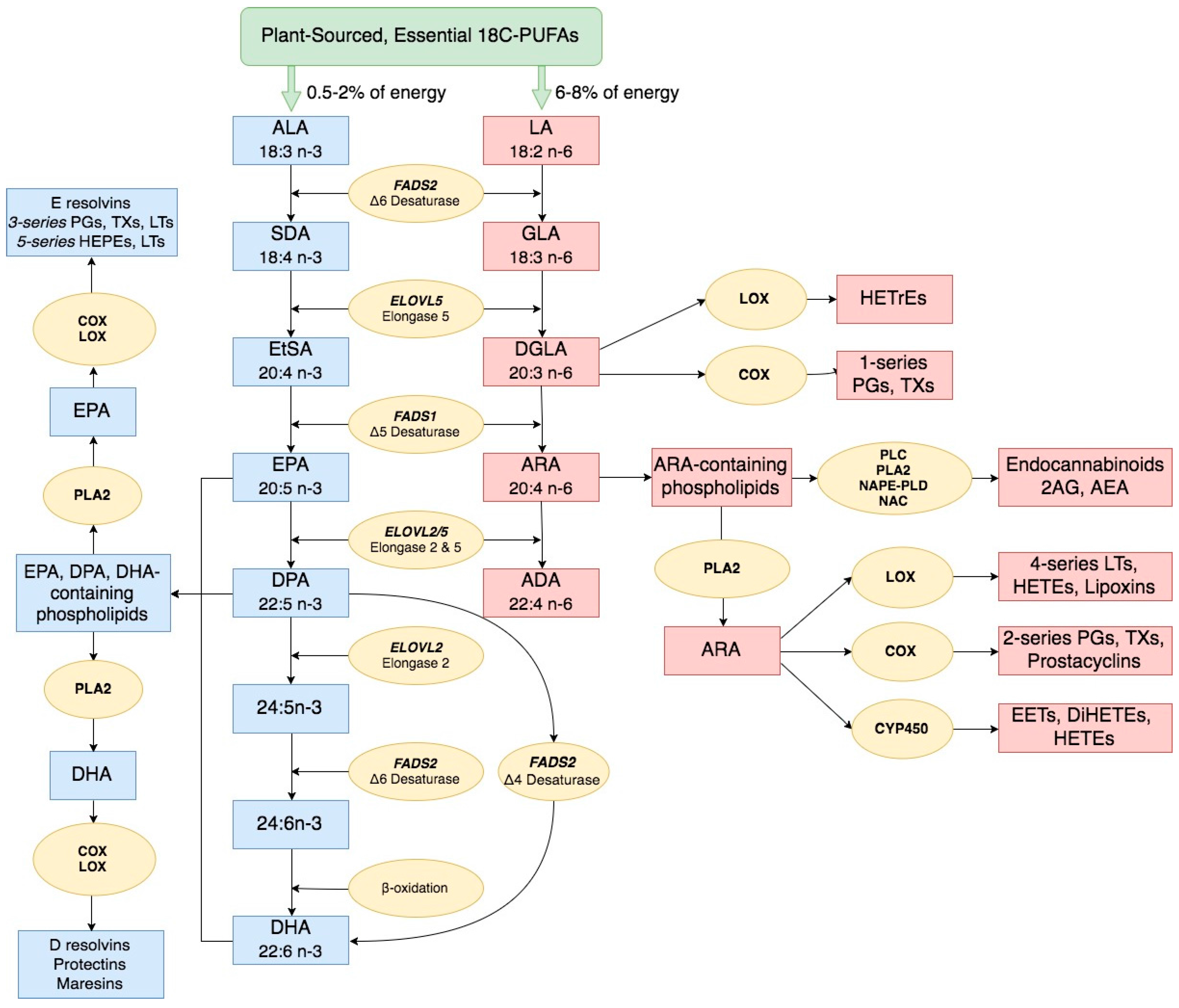
- The Omega-3 pathway gives rise to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
- The Omega-6 pathway gives rise to γ-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA), arachidonic acid (ARA), adrenic acid (ADA). Ultimately, the inflammatory metabolites include: prostaglandin (PG), thromboxane (TX), leukotriene (LT).
Le HD, Fallon EM, Kalish BT, de Meijer VE, Meisel JA, Gura KM, Nose V, Pan AH, Bistrian BR, Puder M. The effect of varying ratios of docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid in the prevention and reversal of biochemical essential fatty acid deficiency in a murine model. Metabolism. 2013 Apr;62(4):499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2012.10.003. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PubMed PMID: 23151438; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3608741.
Chilton FH, Dutta R, Reynolds LM, Sergeant S, Mathias RA, Seeds MC. Precision Nutrition and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Case for Personalized Supplementation Approaches for the Prevention and Management of Human Diseases. Nutrients. 2017 Oct 25;9(11). pii: E1165. doi: 10.3390/nu9111165. Review. PubMed PMID: 29068398; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5707637
- Scaly skin
- Growth failure
- Alopecia
HOLMAN RT. The ratio of trienoic: tetraenoic acids in tissue lipids as a measure of essential fatty acid requirement. J Nutr. 1960 Mar;70:405-10. PubMed PMID: 14402760.
|
- anemia, leukopenia,
- thrombocytopenia
- fibrinogen
- coagulopathy
- acidosis.
Lab monitoring:
- Oxygen saturation
- CBC with platelets
- Liver panel
- Chem-10
- Coagulation profile, fibrinogen
- Triglycerides
- Amylase, lipase.
- If triglycerides are elevated, repeat in 4 hours.
-
Supportive care
-
Withhold lipids
-
Supplemental oxygen
-
FFP
-
Vitamin K
-
Blood transfusions
Hojsak I, Kolaček S. Fat overload syndrome after the rapid infusion of SMOFlipid emulsion. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014 Jan;38(1):119-21. doi: 10.1177/0148607113482001. Epub 2013 Mar 21. PubMed PMID: 23520135.
Gura KM, Puder M. Rapid infusion of fish oil-based emulsion in infants does not appear to be associated with fat overload syndrome. Nutr Clin Pract. 2010 Aug;25(4):399-402. doi: 10.1177/0884533610373770. PubMed PMID: 20702846.
Hayes BD, Gosselin S, Calello DP, Nacca N, Rollins CJ, Abourbih D, Morris M, Nesbitt-Miller A, Morais JA, Lavergne V; Lipid Emulsion Workgroup. Systematic review of clinical adverse events reported after acute intravenous lipid emulsion administration. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016 Jun;54(5):365-404. doi:10.3109/15563650.2016.1151528. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Review. PubMed PMID: 27035513.
|
Product
|
Intralipid
|
Liposyn II
|
ClinOleic
|
SMOF lipid
|
Omegaven
|
|
Manufacturer
|
Baxter Healthcare/Fresenius Kabi
|
Hospira
|
Baxter Healthcare/Parenteral SA
|
Fresenius Kabi
|
Fresenius Kabi
|
|
Oil source (g)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Soy bean
|
10
|
5
|
2
|
3
|
0
|
|
Safflower
|
0
|
5
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
MCT
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
3
|
0
|
|
Olive oil
|
0
|
0
|
8
|
2.5
|
0
|
|
Fish oil
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
1.5
|
10
|
|
α -Tocopherol (mg/L)
|
38
|
NP
|
32
|
200
|
150-296
|
|
Phytosterols (mg/L)
|
348 ± 33
|
383
|
327± 8
|
47.6
|
0
|
|
Fat composition (g)a
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Linoleic
|
5
|
6.5
|
0.9
|
2.9
|
0.1- 0.7
|
|
α-Linolenic
|
0.9
|
0.4
|
0.1
|
0.3
|
|
|
EPA
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0.3
|
1.28 -2.82
|
|
DHA
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0.05
|
1.44-3.09
|
|
Oleic
|
2.6
|
1.8
|
0.8
|
2.8
|
0.6 - 1.3
|
|
Palmitic
|
1
|
0.9
|
0.7
|
0.9
|
0.25 -1
|
|
Stearic
|
0.35
|
0.34
|
0.2
|
0.3
|
0.05-0.2
|
|
Arachidonic
|
0
|
0
|
0.03
|
0.05
|
0.1-0.4
|
