Discharge Criteria for new HPN referral
Discharge Criteria for new HPN referral
|
Patient selection: 2 weeks before discharge |
|
HPN Team consulted by primary service. Primary GI, inpatient nutrition attending and inpatient dietitian agrees to referral. |
|
Defined indication for HPN (e.g., SBS, severe malabsorption, fistula, GI obstruction, IBD, motility disorder, swallowing disorders) |
|
Enteral feeds tried and failed, or enteral feeds contraindicated |
|
Anticipated PN duration ≥ 4 weeks |
|
Underlying disease is stable. HPN is contraindicated for severe cardiopulmonary disease, unstable endocrinopathy, severe immunodeficiency, life-expectancy |
|
Caregivers/patient provides verbal consent for HPN |
|
Medical clearance: 1-2 weeks before discharge |
|
Weight ≥ 5 kg |
|
Central venous catheter tip in SVC/IVC or cavoatrial junction as documented on X-ray at BCH within 1 year if 2 years-old. |
|
Afebrile ( |
|
IV medications other than PN ≤ 2 times/day. |
|
Attention to medication-PN compatibility. IV lipids may need to be held. |
|
Social work and case management clearance |
|
Caregiver with appropriate domicile (Clean space, storage for supplies, working refrigeration (separate from community, phone, running warm water, electricity) |
|
Health insurance in place for HPN and outpatient follow-up. |
|
Caregiver/patient able to follow up in HPN program within 1 month, or X1/weekly if OM + direct bilirubin ≥ 2. (Distance, transportation, work/school schedule, means, collaborating other providers.) |
|
Home services established (Home infusion company, nursing). |
|
Parenteral nutrition regimen optimal at discharge: |
|
PN cycled to ≤ 20 hours. |
|
SMOFlipids for long-term PN considered, soybean-based IV lipids ≤ 1 gram/kg/day) and Compassionate-Use Omegaven considered for PNALD. |
|
PN regimen unchanged for ≥ 3 days |
|
Labs within expected range |
|
Infusion rates of Intralipids and potassium in acceptable range (IL |
|
If iron deficient and needing home IV iron, test dose has been tolerated inpatient |
|
Meeting hydration, macro and micronutrient goals with present PN regimen |
|
Weight trend in acceptable range. |
|
HPN teaching complete |
|
Patient/caregiver demonstrates competent central venous catheter care (Washing hands, putting on mask, wearing sterile gloves, scrubbing hub, flushing catheter, changing central line cap, changing dressing). |
|
There are 2 adults trained for central line care (not including VNA). |
|
Outpatient coordination in place |
|
Outpatient labs plan agreed upon by patient/caregiver and inpatient team (location, timing, frequency). Maximum frequency ≥ 1 time/week, goal to space out over time (typically once per month). |
|
Outpatient HPN appointment booked. |
|
If long-distance, local provider identified PMD, local GI, surgeon to facilitate tests, home care orders. |
New Patient Discharge Timeline
|
2 weeks prior to discharge |
HPN consult (MD & NP) |
|
1-2 weeks prior to discharge |
HPN teaching (RN) |
|
1-5 days prior to discharge |
SimLab (RN, SimLab staff) |
|
1-3 days prior to discharge |
Pre-discharge briefing (HPN team, case management, nursing and primary team) |
|
Discharge day |
Wrap up session (HPN team) |
|
Post-discharge day 1-3 |
Telemedicine visit (HPN team) |
|
1-2 weeks post-discharge |
HPN visit (HPN RN emphasis) |
|
1 month post-discharge |
Social Media
- Picture's worth 1,000 words.
- HPN families can use pictures to learn & remember all sorts of concepts.
- Speak up if you think an illustration might help to explain something -- e.g. central line flushing, liver anatomy, IV lipid types, PN tubing hook-up (below)."

Social Media
- Personally obtain copies of discharge summary.
- Review information for accuracy, especially prescriptions!
- Forward summary directly to your HPN team.
- Request attending physician-to-physician sign-out."

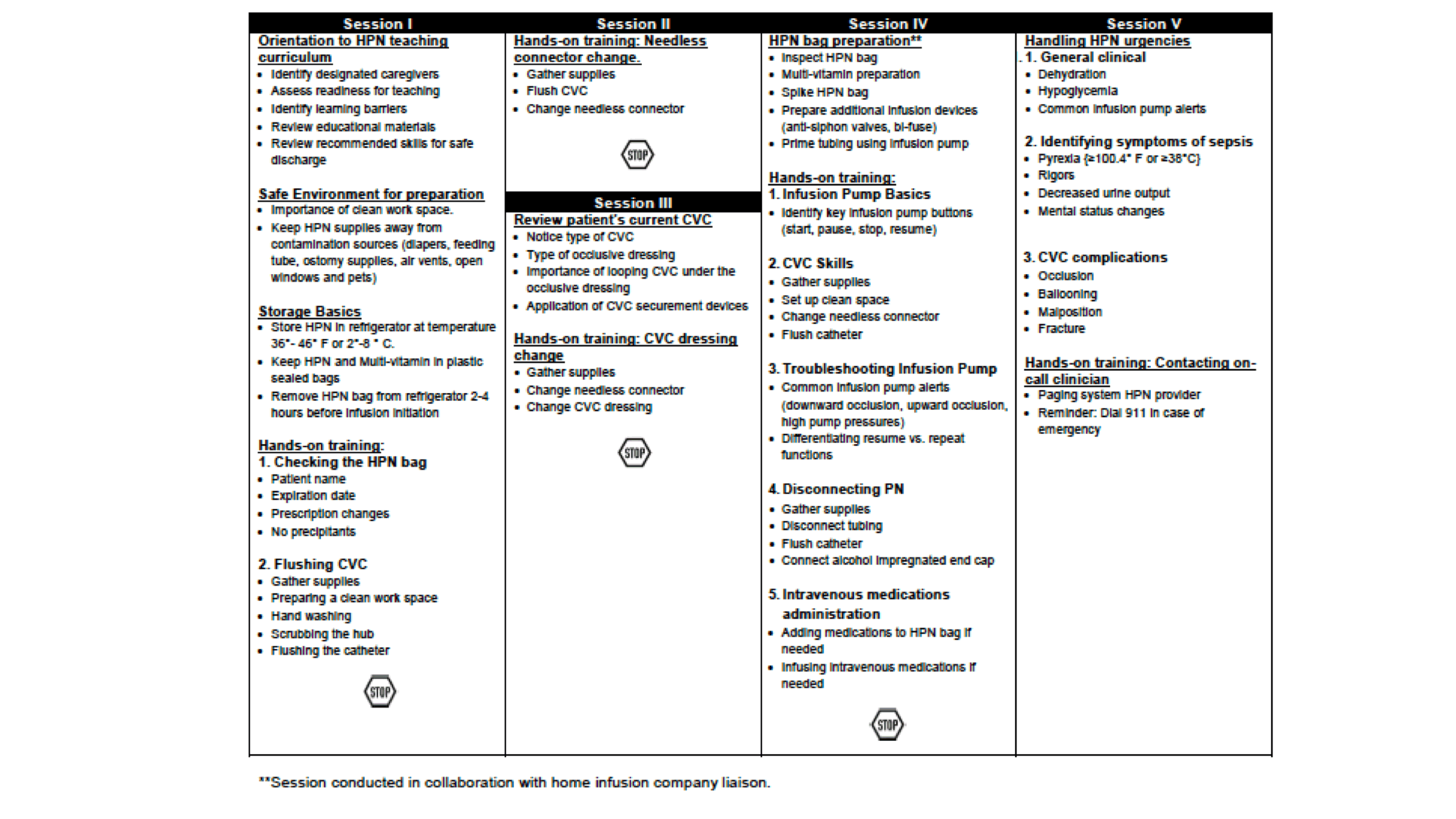
Five-session teach developed by Mary Gallotto: Prior to hospital discharge, the home parenteral nutrition nurse leads caregiver through standardized HPN curriculum over five sessions with increasingly complex tasks using low-fidelity simulation mannequin, including central venous catheter (CVC), CVC supplies as well as infusion pump equipment
Click here for related Clinical Vignette
Special discharges:
Discharging HPN patient who is NPO:
- Make sure definite medical indication for NPO status.
- Ensure patient maintains blood sugar and hydration while inpatient cycling.
- Prescribe and teach caregiver to use glucometer.
- Consider prescribing glucagon.
ESPEN guidelines for Adults with Intestinal Failure
Discharging HPN patient who is receiving IV antibiotics:
- Antibiotic frequency (maximum frequency every 8 hours).
- Pre-medications needed (orally versus IV).
- PN and IV lipid compatibility of antibiotics.
- Administration device (syringe pump, ball).
- Tubing (bifuse).
- Laboratory coordination (electrolytes, repeat blood cultures).
- Counseling parents to monitor for side-effects on IV antibiotics.
-
What happened?
-
Was communication clear?
-
Were roles and responsibilities understood?
-
Was situation awareness maintained?
-
Was workload distribution equitable?
-
Was task assistance requested or offered?
-
Were errors made or avoided?
-
Were resources available?
-
What should improve?
Challenge Point Framework of Teaching:


Guadagnoli MA, Lee TD. Challenge point: a framework for conceptualizing the effects of various practice conditions in motor learning. J Mot Behav. 2004 Jun;36(2):212-24. PubMed PMID: 15130871.